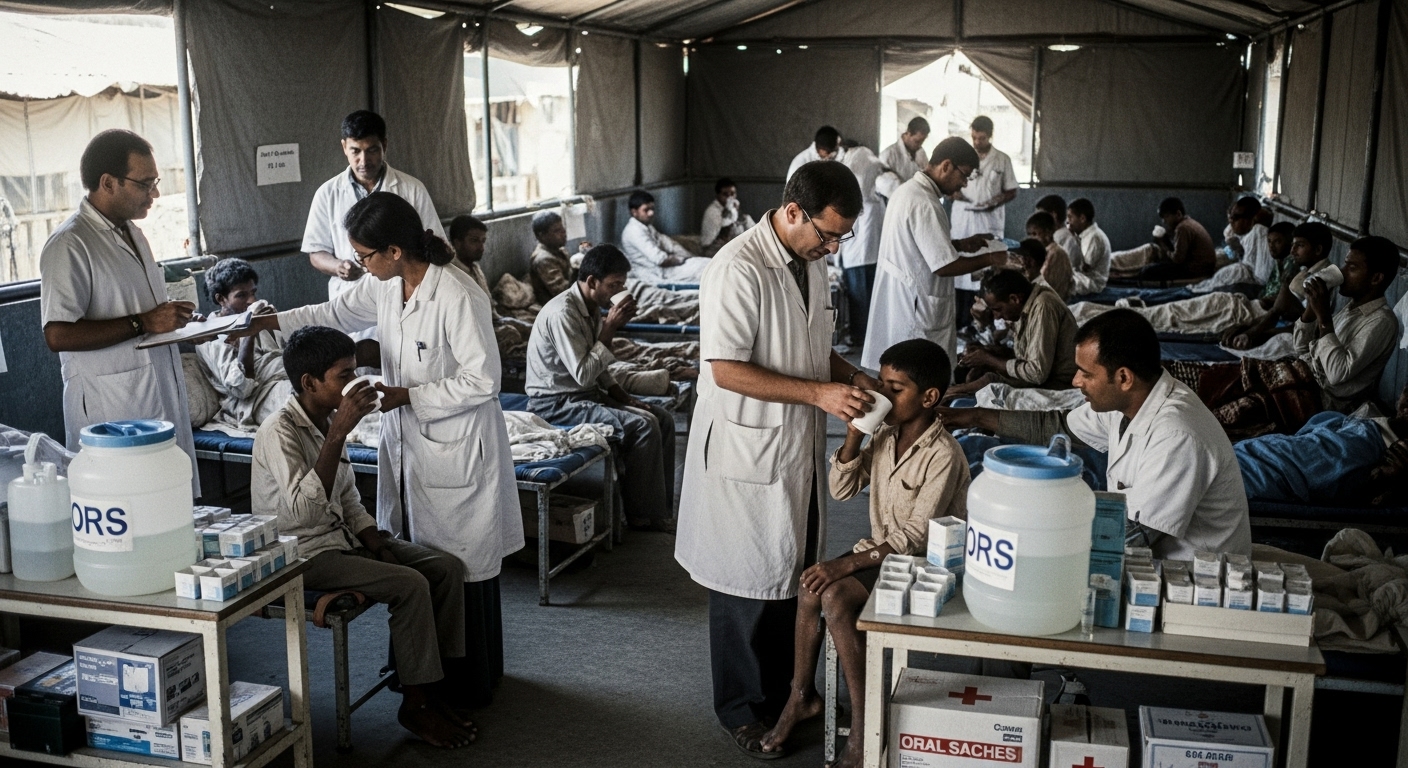
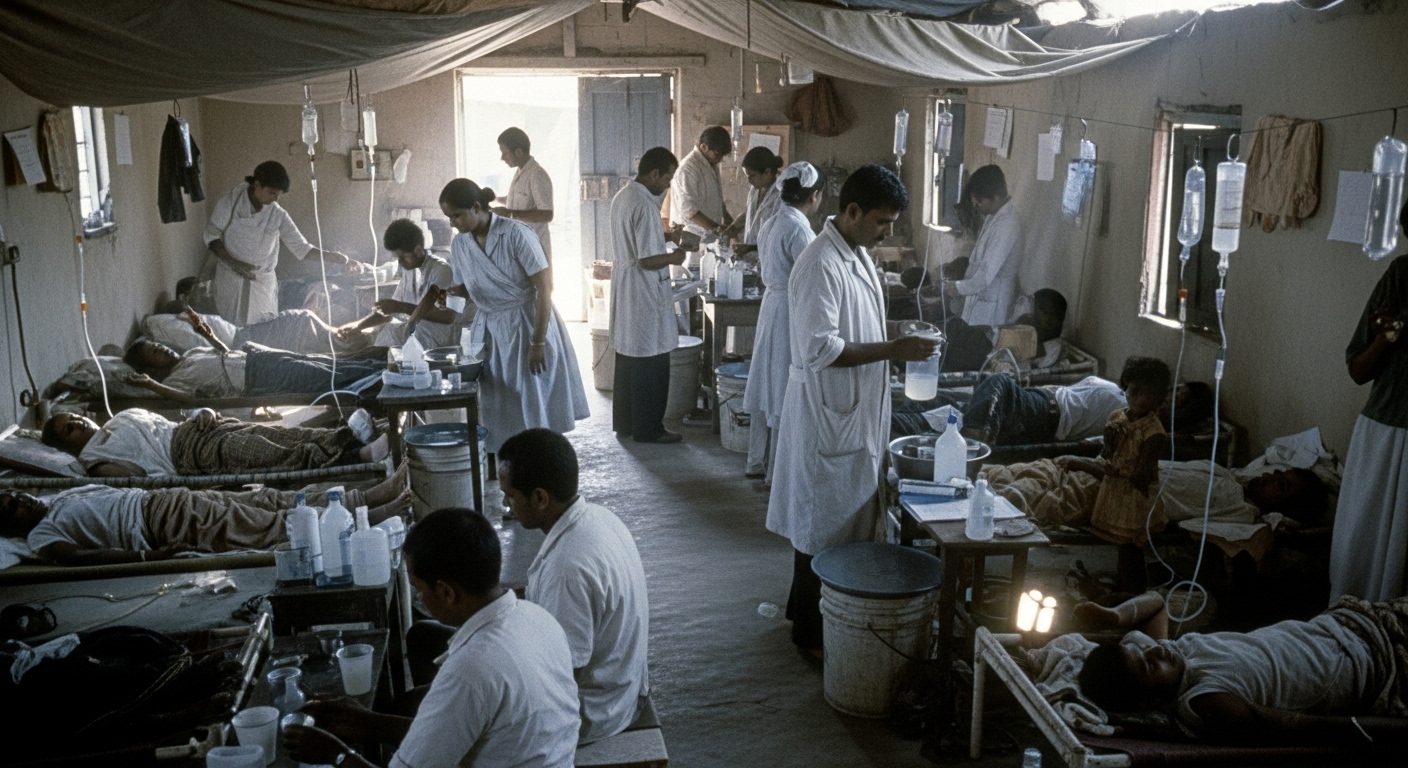
Oral Fluid Therapy of Cholera among Bangladesh Refugees (WHO Study)
Dr. Kumar’s Take:
During the Bangladesh refugee crisis, cholera spread through crowded camps, overwhelming hospitals and supply chains. This WHO-led field trial showed that a simple oral solution, mixed and administered on-site, could save lives at scale. It was one of the first demonstrations that oral rehydration could be deployed under extreme field conditions.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Oral rehydration therapy was effective even in large refugee populations.
✔ Mortality fell dramatically when oral fluids were introduced early.
✔ Local volunteers were trained to mix and deliver the solution safely.
✔ This study proved ORT was scalable, not just clinically effective.