How Proton Pump Inhibitors Work: Complete Pharmacology Guide
How Do Proton Pump Inhibitors Actually Work at the Molecular Level?
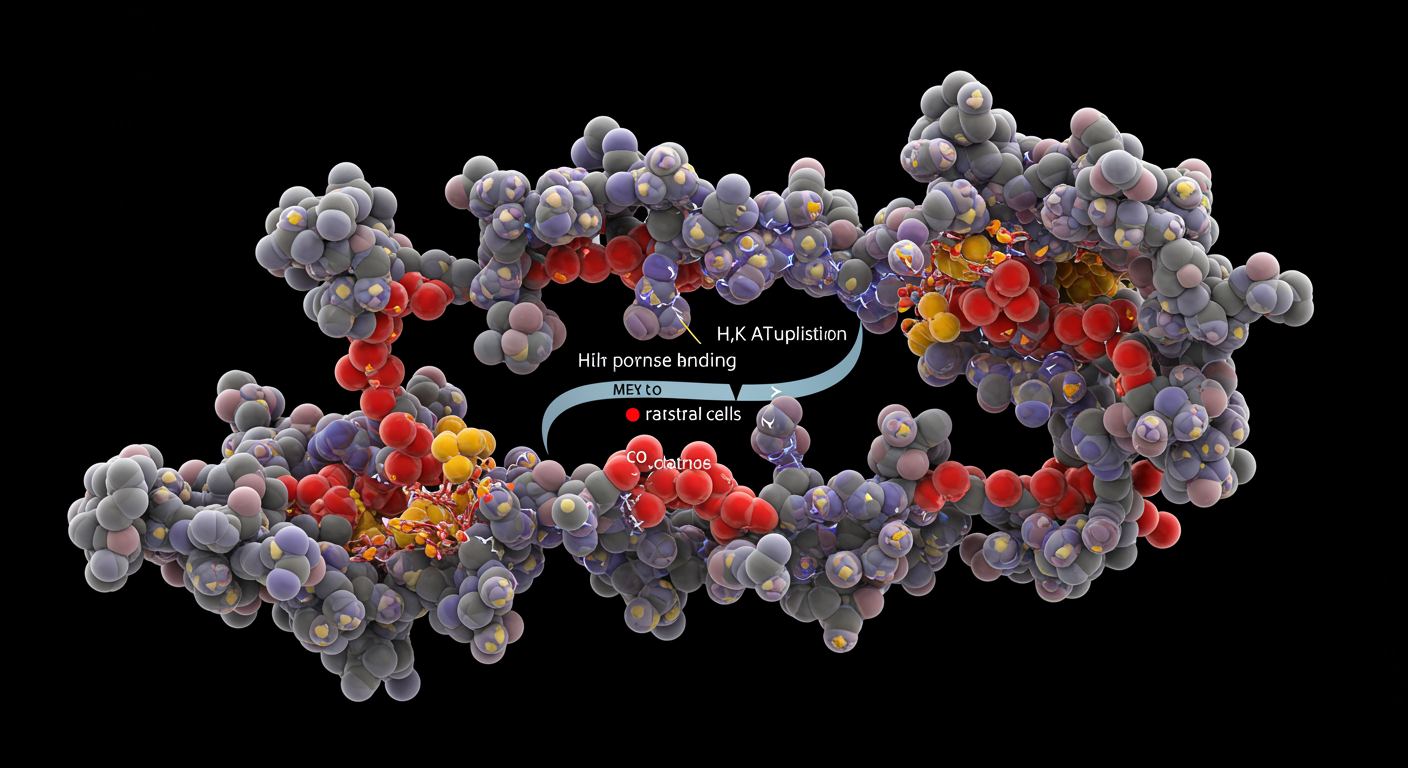
Proton pump inhibitors work by irreversibly binding to and inactivating the H,K-ATPase enzyme (proton pump) in gastric parietal cells, which is the final common pathway for all gastric acid production. These medications are prodrugs that become activated only in the acidic environment of the parietal cell secretory canaliculus, where they form covalent bonds with specific cysteine residues on the proton pump, permanently disabling individual enzyme molecules until new pumps are synthesized.